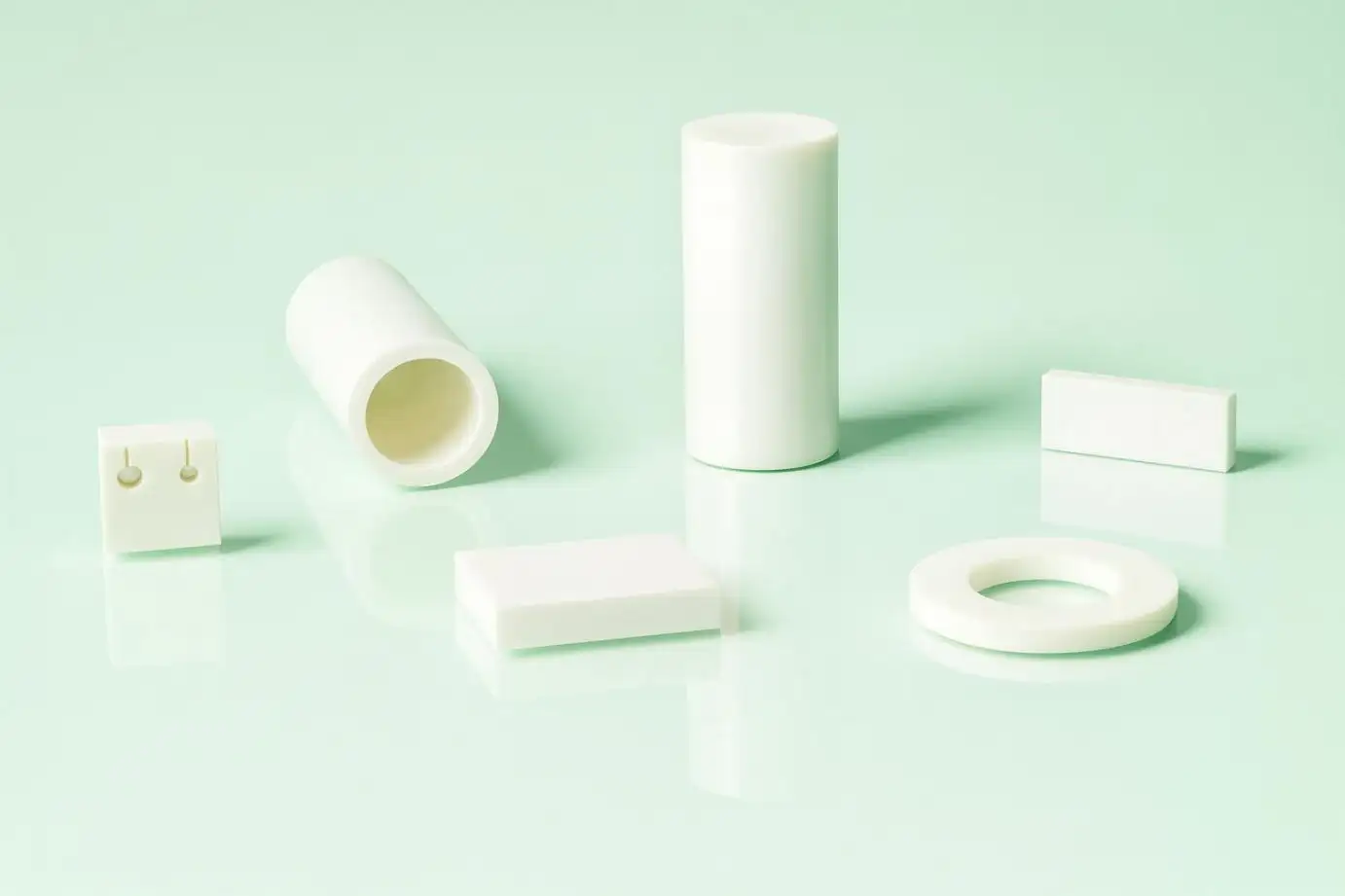
Ceramic Tube Sleeves Supplier Indonesia
Finding a specialized supplier for ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia is a critical task for many high-temperature industries. These components are essential for thermal management, electrical insulation, and material protection. Ceramic tubes and sleeves are engineered materials. They are designed to perform in harsh environments where metals and plastics fail. Their properties include extreme heat resistance, chemical inertness, and high dielectric strength.

The term "ceramic sleeve" can refer to two different product categories. One category is industrial tubes for furnaces and processing. The other is high-temperature flexible fiber sleeves. This guide will explore both types. It will detail their materials, applications, and manufacturing. It will also clarify the difference between these industrial products and the precision components used in other fields. Understanding these distinctions is key to sourcing the correct part.
Understanding Industrial Ceramic Tubes
Industrial ceramic tubes are rigid, hollow-core components. They are designed for structural, protective, or containment purposes. Unlike metal pipes, ceramic tubes do not corrode. They maintain their strength at very high temperatures. A supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia provides these parts to foundries, chemical plants, and furnace manufacturers.
What Are Industrial Ceramic Tubes?
An industrial ceramic tube is a component formed from technical ceramics. Common materials include alumina, mullite, or silicon carbide. They are fired at high temperatures to create a dense, hard, and stable structure. These tubes can be large in diameter. They are often used as furnace liners, thermocouple protection tubes, or rollers for moving hot materials.
The Function of a Ceramic Sleeve
A ceramic sleeve, in an industrial context, often acts as a liner or a shield. It can be a rigid tube inserted into a larger assembly to protect it. For example, a sleeve can protect a metal rod from molten metal. It can also act as an electrical insulator, separating conductive parts in a high-voltage system. The specific function dictates the material choice and the dimensional precision required.
Key Differences: Industrial vs. Precision Sleeves
It is essential to distinguish industrial tubes from precision sleeves. A general ceramic sleeves guide may cover all types, but their applications are not interchangeable. A supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia typically focuses on industrial-grade products.
Precision Zirconia Sleeves for Optics
This is a separate category. High precision ceramic sleeves are tiny components. They are used in the telecommunications industry. Their purpose is to align optical fibers. These sleeves are defined by sub-micron tolerances. They are made from a specific material: zirconia. A zirconia ceramic sleeve is a hard, dense part. It is polished to a mirror finish. This is a high-tech component for data, not heat.
High-Temperature Ceramic Fiber Sleeves
This is the second category of industrial sleeves. These are not rigid tubes. They are flexible, woven sleeves. They are made from ceramic fibers, such as alumina-silica. These sleeves are used for insulation. They are wrapped around pipes, cables, or hoses. We protect them from extreme heat, sparks, and molten metal splash. They are soft and can be cut to length.
Summary of Component Types
- Ceramic Tubes: Rigid, dense, hard. Made from alumina, mullite, etc. Used for furnace parts, protection tubes, and rollers.
- Ceramic Fiber Sleeves: Flexible, soft, woven. Made from alumina-silica fibers. Used for heat insulation and cable protection.
- Precision Zirconia Sleeves: Rigid, dense, tiny. Made from zirconia. Used for fiber optic alignment.
A top supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia should clarify which product a customer needs.
Core Materials for Rigid Ceramic Tubes
The performance of a ceramic tube is defined by its material. Each material offers a different balance of thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina (Al2O3) is the most common technical ceramic. It is valued for its high strength, wear resistance, and excellent electrical insulation. The purity of the alumina is important.
- 95% Alumina: A good all-purpose material.
- 99% - 99.8% Alumina: This high-purity grade offers better chemical resistance. It has a higher working temperature. It is often used for semiconductor and lab equipment.
Alumina tubes are popular as furnace process tubes, insulators, and thermocouple sheaths.
Mullite (Aluminosilicate)
Mullite is another aluminosilicate material. Its primary feature is excellent thermal shock resistance. This means it can be heated and cooled quickly without cracking. It also has good strength at high temperatures. Mullite tubes are often used as kiln furniture, rollers, and structural supports inside furnaces.
Cordierite
Cordierite is known for its extremely low thermal expansion. This gives it the best thermal shock resistance of all. It is not as strong as alumina. It is not used for high-wear applications.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is a premium performance material. It has outstanding thermal conductivity. This allows it to transfer heat very well. It is also extremely hard and wear-resistant. It maintains its strength at very high temperatures. SiC tubes are used in demanding applications. This includes radiant heater tubes and components for chemical processing.
The Market for Ceramic Fiber Sleeves
A supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia often also provides flexible fiber sleeves. These products serve the insulation and personal protection markets.
What Is a Ceramic Fiber Sleeve?
A ceramic fiber sleeve is a woven textile product. It is produced from yarn made of high-purity alumina-silica fibers. These are often called Refractory Ceramic Fibers (RCF). The yarn is braided or woven into a hollow, flexible sleeve. These sleeves can often be reinforced with fiberglass or steel wire.
Properties of Ceramic Fiber
The key property of a ceramic fiber sleeve is its low thermal conductivity. It is an excellent insulator. It traps air within its fibers. This prevents heat transfer. It is lightweight, flexible, and chemically stable. It is resistant to oil, water, and most chemicals.
Applications in High-Temperature Industries
Ceramic fiber sleeves are used for protection.
- Hose and Cable Protection: They are slipped over critical hoses and cables. This shields them from molten metal splash, welding sparks, and radiant heat.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The same material is used to make gloves, blankets, and aprons.
- Gaskets and Seals: Woven fiber can be used as a high-temperature gasket.
Sourcing these flexible materials, like ceramic fiber components Indonesia, is a key service.
Sourcing from a Ceramic Tube Supplier
Working with a ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia supplier requires a focus on technical details. This is not a commodity product.
What to Look for in a Supplier
A premium supplier provides more than just a part. They provide technical support and quality assurance.
- Technical Expertise: The supplier should have engineers. They must understand the material properties. They should be able to recommend the right ceramic for the application.
- Material Certification: The supplier must provide material datasheets. These documents prove the composition, purity, and properties of the ceramic.
- Quality Control: The supplier must have an inspection process. They must check for dimensional accuracy, cracks, and porosity.
- ISO 9001 Certification: This standard shows the supplier has a documented quality management system.
The Importance of a Local Distributor
A local distributor in the region is a valuable asset. They manage the complexities of importing these heavy, fragile parts. They hold local stock. This reduces lead times from months to days. They understand the local market needs. They can provide on-site support.
When sourcing industrial tubes, key questions must be asked.
- What is the maximum working temperature of this tube?
- What is the material's thermal shock resistance?
- What are the dimensional tolerances? (e.g., ±1% on diameter).
- Can this material handle a corrosive atmosphere?
The answers will guide the selection process.
Key Applications of Ceramic Tubes and Sleeves
These components are used across every heavy industry. Their primary purpose is to allow processes to run at high temperatures.
Thermal Insulation and Protection
This is the most common use. Ceramic fiber sleeves are wrapped around pipes. Rigid ceramic tubes are used as liners in furnaces. They protect the outer steel shell from the internal heat. This improves the furnace's energy efficiency.
Electrical Insulation
Alumina is an excellent electrical insulator. It does not conduct electricity, even at high temperatures. Ceramic tubes are used as insulators in spark plugs. They are also used in high-voltage equipment to support and separate conductors.
Molten Metal Handling
Ceramics are non-reactive with most molten metals. Tubes made of silicon carbide or alumina are used to transport liquid metal. They are also used as protection sheaths for thermocouples. A thermocouple must measure the temperature of the metal bath. The ceramic tube protects the sensor from being destroyed.
Furnace and Kiln Components
Ceramic tubes are the building blocks of electric furnaces.
- Process Tubes: A gas or a product can be passed through a ceramic tube. The tube is heated from the outside.
- Element Supports: Ceramic tubes and rods are used to hold the metal heating elements. They insulate the elements from the furnace body.
- Rollers: In a continuous furnace, ceramic rollers are used. They transport the product (like glass or steel) through the hot zone.
The Manufacturing Process for Ceramic Tubes
Understanding how a tube is made helps in sourcing. The process determines the final properties.
Extrusion and Forming
Most ceramic tubes are made by extrusion. The ceramic powder is mixed with a binder and water. This creates a stiff, clay-like paste. This paste is forced through a die. A die is a steel tool with a circular opening. A center pin in the die creates the hollow tube. This process creates a long, continuous "green" tube. It is then cut to length.
Sintering and Firing
The green tubes are very fragile. They must be dried carefully. After drying, they are placed in a large kiln. They are fired at an extremely high temperature. This temperature is often over 1,600°C. This firing process is called sintering. The ceramic particles fuse. The tube shrinks. It becomes hard, dense, and strong.
Finishing and Grinding
For many industrial uses, the "as-fired" tube is precise enough. However, some applications need tighter tolerances. For these, the tube must be "hard-ground." This is a slow, expensive process. It uses diamond-coated tools. Grinding can achieve very precise diameters. It can also create a smooth, polished surface.
Quality Assurance for Industrial Ceramics
A supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia must verify the quality of their products.
Material Purity and Density
The supplier must verify the chemical composition. This is done through lab analysis. They also check the density. A low-density part (with high porosity) will be weak. It will not have good thermal properties.
Dimensional Accuracy
Inspectors measure the tube's dimensions. They check the inner diameter, outer diameter, and length. They also check for straightness. A long tube that is not straight cannot be used as a roller.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Good suppliers will have data on thermal shock. This is the material's ability to survive rapid temperature changes. They test this by heating a part. Then, they plunge it into cool water. They check for cracks.
Comparing Global Manufacturing Hubs
The market for industrial ceramics is global. Different regions are known for different strengths.
- High-purity, specialized components are often sourced from advanced economies. Producers of ceramic fiber sleeves Japan are known for their quality.
- High-volume and standard industrial ceramics are produced in many regions.
A supplier of ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia must manage this global supply chain. They find the best-value manufacturer for a specific quality level. The market for ceramic fiber components Indonesia is also growing. This meets the local demand from refineries, power plants, and manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Value of a Specialist Supplier
Ceramic tubes and sleeves are not simple products. They are engineered components. The difference between alumina and mullite, or a rigid tube and a fiber sleeve, is vast. Sourcing these parts requires technical knowledge.
A premium ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia supplier is a partner. They are a local source of engineering support. They manage a complex global supply chain. We hold local inventory to reduce lead times. They perform quality control to ensure every part meets its specification. For any industry working with high temperatures, this partnership is essential for success.
- PREV: Ceramic Fiber Components Manufacturer Indonesia
- NEXT: Null
In This Article
- 1 Understanding Industrial Ceramic Tubes
- 2 Key Differences: Industrial vs. Precision Sleeves
- 3 Core Materials for Rigid Ceramic Tubes
- 4 The Market for Ceramic Fiber Sleeves
- 5 Sourcing from a Ceramic Tube Supplier
- 6 Key Applications of Ceramic Tubes and Sleeves
- 7 The Manufacturing Process for Ceramic Tubes
- 8 Quality Assurance for Industrial Ceramics
- 9 Comparing Global Manufacturing Hubs
- 10 Conclusion: The Value of a Specialist Supplier
 English
English 中文
中文