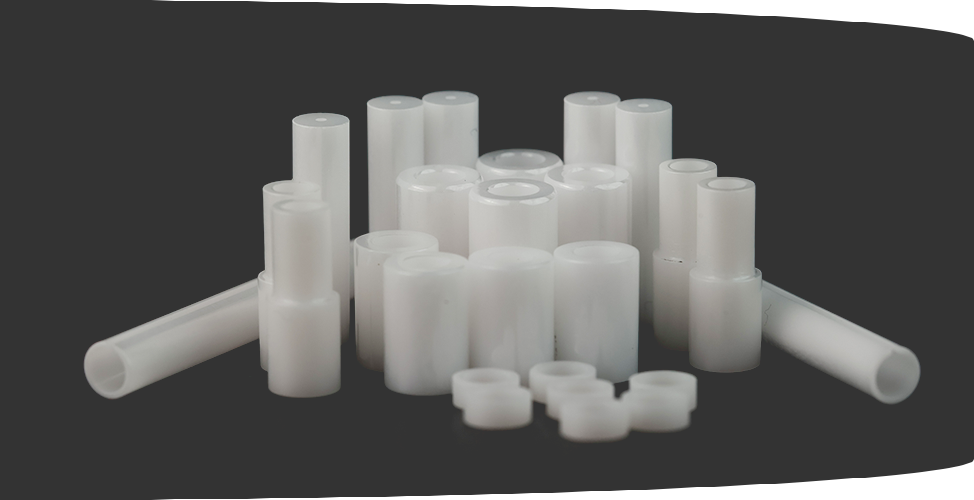
Alumina Ceramic Rod Supplier
A premier alumina ceramic rod supplier is a cornerstone of modern industry. These specialized suppliers provide high-performance components made from aluminum oxide (Al2O3). This material is one of the most versatile and widely used technical ceramics. It is valued for its exceptional combination of properties. This includes high-temperature stability, electrical insulation, and wear resistance. Industries from manufacturing to aerospace rely on these components.

A professional supplier is more than just a reseller. They are a technical partner. They provide a vital link in the supply chain. We connect the complex world of ceramic manufacturing with the practical needs of engineers. A top-tier supplier ensures material quality, manages logistics, and provides critical expertise. This article explores the world of alumina ceramic rods. It details the material, its applications, and the role of a quality supplier.
What Are Alumina Ceramic Rods?
Alumina ceramic rods are dense, cylindrical components. They are engineered from high-purity aluminum oxide powder. They are not the same as traditional pottery. We are advanced materials. They are designed for function in extreme environments. Metals and plastics often fail in these conditions. Alumina rods thrive.
Defining the Material: Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
Aluminum oxide is the most common technical ceramic. This is due to its excellent properties. It also has a very cost-effective price point. It is a hard, chemically stable, and non-conductive material. We can be manufactured to a high degree of precision. These rods can be solid cylinders or hollow tubes.
The Importance of Material Purity
The properties of an alumina rod are directly tied to its purity. A premier alumina ceramic rod supplier will offer several grades.
- 95% Alumina: This is a common industrial grade. It has a good balance of properties. It is used for wear parts, seals, and structural components.
- 99% Alumina: This grade offers better electrical insulation. It also has higher wear resistance. It is often used in electronics.
- 99.5% Alumina: This is a high-performance grade. It has excellent strength and a very fine grain size.
- 99.9%+ Alumina: This is an ultra-pure grade. It is used in semiconductor and medical applications. It offers superior chemical resistance.
Key Properties at a Glance
A supplier provides materials with a defined set of properties. For alumina, these include:
- High working temperatures (up to 1700°C).
- High dielectric strength (excellent electrical insulation).
- High hardness and wear resistance (Mohs 9).
- Good corrosion resistance to most acids and alkalis.
- High compressive strength.
Alumina Rods vs. Alumina Tubes
It is important to distinguish between rods and tubes.
- Rods: These are solid cylinders. They are used for structural supports, shafts, and electrical insulators.
- Tubes: These are hollow cylinders. They are used to protect components. This includes thermocouple sheaths or laser cavities.
A full-service supplier will offer both products.
The Critical Role of a Premier Alumina Ceramic Rod Supplier
A supplier is a critical link in the supply chain. They provide services that are just as important as the product itself.
More Than Just a Reseller
A simple reseller just moves a box. A premier supplier is a technical partner. They add value at every step. They help customers select the right material. We also help them navigate complex sourcing.
Technical Expertise and Engineering Support
A top supplier has engineers and material scientists on staff. They are not just salespeople. They can read a technical drawing. We can discuss an application's specific challenges.
- Material Selection: They help customers choose the right purity. Is 95% alumina sufficient, or is 99.5% needed? This decision impacts cost and performance.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): A customer may design a custom part. The supplier's engineers can review the design. They can suggest changes. This can make the part stronger. It can also make it more cost-Peffective to produce.
- Troubleshooting: If a component fails, the supplier can help. They can analyze the failure. They can recommend a better material.
Managing Logistics and Local Inventory
This is a primary function of a top supplier. Manufacturing advanced ceramics is a long process. Lead times from a factory can be 12-16 weeks. An industrial plant cannot wait that long for a spare part.
- Local Stockholding: A premier supplier invests in a large, local warehouse. They stock millions of standard-sized rods.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Delivery: Customers can pull stock as needed. This reduces their own inventory costs. It ensures they get parts in days, not months.
- Global Logistics Management: The supplier handles all importation. This includes customs, duties, and international freight.
The Supplier as a Quality Assurance Partner
This is the supplier's most important role. The global market has many manufacturers. The quality of their products can vary widely. A premier supplier acts as the quality firewall.
- Vetting Manufacturers: They audit their manufacturing partners. They inspect their facilities. They verify their ISO 9001 certifications.
- In-House Metrology: A top supplier has its own quality lab. They do not just trust the factory's report.
- Batch Testing: They take samples from incoming shipments. They check them for dimensions, density, and defects.
- Rejecting Bad Parts: They identify and reject any components that do not meet specification. This protects the customer.
Deep Dive: The Properties of Alumina Ceramics
An alumina ceramic rod supplier provides a material defined by its superior properties. Understanding these properties is key to its proper application.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Alumina is a refractory material. This means it is stable at very high temperatures.
- Maximum Use Temperature: High-purity alumina can be used continuously. This can be at 1600°C to 1700°C. It will not melt or deform.
- Thermal Conductivity: Alumina is a good thermal conductor. This is unusual for a ceramic. It can dissipate heat. This makes it useful for heat sinks. It is not a thermal insulator like zirconia.
- Thermal Shock: Alumina has moderate thermal shock resistance. It can crack if heated or cooled too quickly.
High Hardness and Wear Resistance
This is one of alumina's most famous traits.
- Hardness: Alumina is extremely hard. It is a 9 on the Mohs scale. Diamond is a 10. This makes it one of the hardest materials.
- Wear Resistance: Because it is so hard, it is very resistant to abrasion. It is used for nozzles, guides, and liners. It will outlast hardened steel by many times.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
This property is vital for many applications.
- High Dielectric Strength: Alumina can withstand a very high voltage. It does not conduct electricity.
- High Resistivity: It resists the flow of current.
- Low Dielectric Loss: It is efficient as an insulator, even at high frequencies.
This combination makes it the ideal material for high-voltage insulators. It is also used for electronic components.
Chemical Inertness and Corrosion Resistance
Alumina is a very stable oxide. It does not react with most chemicals.
- Acid and Alkali Resistance: It is highly resistant to both strong acids and alkalis. This is especially true for high-purity grades.
- No Corrosion: It does not rust or corrode like metals.
- Molten Metal Resistance: It is used in foundries. It can come into contact with molten metals without reacting.
High Compressive Strength
Alumina is exceptionally strong under compression. It is much stronger than steel in this regard. This makes it ideal for use as structural supports.
Alumina Purity Grades in Detail
The grade of alumina dictates its performance.
- 95% Alumina: This is the most common. The other 5% is a silica/glassy phase. This glass phase helps in sintering. It makes the part cheaper to produce. It has good all-around properties.
- 99.5% Alumina: This grade has much less of the glassy phase. It has higher strength. It has better electrical properties. It has higher wear resistance.
- 99.9% Alumina: This ultra-pure grade is used in semiconductors. It is used in plasma chambers. It has the best chemical resistance.
A good supplier can provide a Technical Data Sheet (TDS) for each grade.
The Manufacturing Process: From Powder to Precision Rod
An alumina ceramic rod supplier must have a deep understanding of manufacturing. This is how they vet their partners.
Phase 1: Raw Material Formulation
The process begins with ultra-pure alumina powder. This powder has a particle size in the sub-micron range. It is mixed with proprietary binders and plasticizers. This creates a consistent, moldable slurry or paste. The quality of this initial mix is critical.
Phase 2: Forming the "Green Part" (Extrusion)
This is the most common method for rods. The ceramic paste is forced through a die. A die is a steel tool with a circular opening. This process is like pushing pasta through a machine. It creates a long, continuous "green" rod. This green rod is then cut to the desired length. For other shapes, Isostatic Pressing is used.
Phase 3: Sintering and Binder Burnout
The green rod is fragile. It is a mix of ceramic powder and binder. It must be fired to become a hard ceramic. This is a two-step thermal process.
- Debinding: The rod is heated slowly, often around 600°C. This process burns away the polymer binder. This must be done gradually. Rushing this step will cause the part to crack or warp.
- Sintering: The temperature is then raised much higher. This is often over 1600°C for alumina. At this heat, the ceramic particles fuse. The part shrinks by 15-25%. It becomes incredibly hard and dense.
Phase 4: Precision Finishing (Diamond Grinding)
After sintering, the rod is "as-fired." Its dimensions are not yet perfect. The tolerances might be ±1%. For high-precision applications, it must be finished. The rod is now extremely hard. It can only be machined with diamond tools. This is called "hard-grinding."
Centerless grinding is the most common finishing step. The rod is spun between diamond-coated wheels. This grinds the outer diameter to a precise, uniform size. It can achieve tolerances of just a few microns. For an even smoother finish, the rod can be lapped.
Alumina Rods in Action: Key Industrial Applications
The unique combination of properties makes alumina rods useful in almost every industry.
High-Temperature Furnace Components
This is a major application for alumina rods.
- Structural Supports: Rods are used as supports, "kiln furniture." They hold products inside a furnace.
- Heating Element Supports: Rods and tubes are used to hold and insulate electric heating elements.
- Thermocouple Sheaths: Hollow rods (tubes) protect temperature sensors.
Electrical Insulation in Power Systems
This is a critical application.
- Standoff Insulators: Alumina rods are used to support high-voltage wires.
- Busbar Supports: They insulate high-voltage bus bars in switchgear.
- Electronic Components: Rods are used as cores for resistors.
Chemical Processing and Fluid Handling
This sector needs corrosion resistance.
- Pump Shafts: In chemical pumps, an alumina rod will outlast a metal shaft. It will not corrode.
- Valve Components: Ceramic balls and seats are used in corrosive-fluid valves.
- Stirrers: A ceramic rod can stir a hot, corrosive chemical solution.
Wear-Resistant Components in Manufacturing
This sector needs hardness.
- Guide Rods and Pins: Alumina rods are used as guides and locating pins in assembly jigs. Their wear resistance ensures a long life.
- Nozzles: Rods are machined into nozzles for sandblasting or spraying.
- Textile Guides: Rods are polished and used as guides for fibers.
Laboratory and Scientific Equipment
- Mortars and Pestles: Alumina is used for its hardness and purity.
- Crucibles: Alumina crucibles are used to melt materials.
- Analysis Tools: Rods are used in thermal analysis equipment.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
High-purity alumina is essential for this industry.
- Plasma Chamber Parts: Alumina is used for components inside semiconductor processing.
- Substrates: Alumina plates are the base for many electronic circuits.
Sourcing High-Strength Ceramic Rods
The term "high strength" is a key specification for these components. It defines their ability to be used in mechanical, load-bearing applications.
What Defines "High Strength" in Alumina?
The strength of alumina is tied to its purity and density. High-purity grades (99%+) have a finer, more uniform grain structure. This makes them stronger. High strength ceramic rods are those made from these advanced grades. They have a higher flexural strength.
Purity, Density, and Flexural Strength
A good supplier will provide a TDS. This sheet will list the "flexural strength" in megapascals (MPa). A high-strength alumina rod will have a high value. This data proves the part's mechanical capability.
Applications for High-Strength Components
These rods are not just insulators. They are structural components. They are used as:
- Shafts: In pumps that move corrosive liquids.
- Plungers: For high-pressure piston pumps.
- Fixtures: In welding and assembly jigs.
Standard vs. Custom Ceramic Rods
A top alumina ceramic rod supplier will offer both standard and custom parts.
What Are Standard Stock Rods?
Standard rods are mass-produced in common diameters. This might be 3mm, 5mm, 10mm, etc. They are sold in standard lengths. They are cost-effective and available for immediate shipment.
The Need for Custom-Engineered Solutions
Many applications cannot use a standard rod. A machine may need a rod with a thread. It may need a specific, odd diameter. This is where custom ceramic rods indonesia and other custom services are needed.
Common Customizations: Threads, Grooves, and Holes
A custom rod is made to a customer's drawing. After sintering, the hard rod is diamond-ground. A custom manufacturer can add features.
- Threads: Internal or external threads can be ground into the rod.
- Grooves: Grooves for o-rings or retaining clips.
- Holes: Cross-drilled holes for pins.
- Flats: Flats can be ground onto the rod for wrenches.
The Custom Manufacturing Process
This is a co-engineering process. The customer provides a drawing. The supplier's engineers perform a DFM review. A prototype is made and approved. Then, full production begins.
An alumina ceramic rod supplier operates in a global market. They must manage a complex supply chain to ensure quality and value.
The Importance of a Diverse Supply Network
A good supplier does not rely on one factory. They have a network of vetted partners. This diversifies risk. It ensures a stable supply.
Sourcing from High-Specification Markets
Some markets are known for their high-specification parts. The ceramic rods usa market, for example, is strong. It focuses on medical, defense, and aerospace applications. A global supplier learns from these standards.
Sourcing from High-Volume Hubs
Other markets have mastered scale. A supplier for industrial ceramic rods china must navigate this hub. This region offers massive capacity and cost-efficiency. A good supplier knows how to find the high-quality producers within this large market.
Understanding Global Quality Benchmarks
A premier supplier benchmarks all parts. They ensure a rod from one factory is identical in quality to a rod from another. This consistency is their promise to the customer.
How to Evaluate an Alumina Ceramic Rod Supplier
Choosing the right partner is critical for success.
ISO 9001:2015 Certification
This is the baseline. Do not work with a supplier who is not ISO 9001 certified. This proves they have a documented quality management system.
Demanding Technical Data Sheets (TDS)
This is the most important document. Always ask for a TDS. This document proves the material's properties. It lists density, hardness, flexural strength, and dielectric strength. It is the guarantee that you are getting what you paid for.
Assessing In-House Metrology and Inspection
Ask the supplier how they check their parts.
- "Do you have an in-house quality lab?"
- "How do you verify the dimensions of a 10,000-piece order?"
- "Can you provide a Certificate of Conformity with my shipment?"
Communication and Engineering Support
A good supplier is a partner. Can you speak to an engineer? Do they respond quickly? Do they understand your technical questions?
Using a Ceramic Rods
A supplier who is an expert will also be an educator. They should provide a ceramic rods. This helps customers make informed decisions.
Innovations in Alumina and Technical Ceramics
The field of ceramics is always advancing. A top supplier will be at the forefront of these innovations.
Pushing Purity and Strength Limits
Manufacturers are constantly improving their processes. They are creating finer powders. This leads to denser, stronger parts.
Advanced Optical Applications
New processing methods can make alumina clear. These Transparent Ceramics are used for high-power lasers. They are also used for scratch-proof lenses.
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs)
These are next-generation materials. They combine ceramic fibers with a ceramic matrix. We are tough and lightweight. They are used in jet engines.
Conclusion
A premier alumina ceramic rod supplier is an essential partner. They are not just a vendor. They are an engineering resource. We are a quality assurance team. They are a logistics expert. They provide the high-performance components that allow modern industry to function. By providing technical support, managing local inventory, and guaranteeing quality, they make advanced materials accessible. They are the foundation of a reliable, high-performance supply chain.
In This Article
- 1 What Are Alumina Ceramic Rods?
- 2 The Critical Role of a Premier Alumina Ceramic Rod Supplier
- 3 Deep Dive: The Properties of Alumina Ceramics
- 4 The Manufacturing Process: From Powder to Precision Rod
- 5 Alumina Rods in Action: Key Industrial Applications
- 6 Sourcing High-Strength Ceramic Rods
- 7 Standard vs. Custom Ceramic Rods
- 8 Navigating the Global Supply Chain
- 9 How to Evaluate an Alumina Ceramic Rod Supplier
- 10 Innovations in Alumina and Technical Ceramics
- 11 Conclusion
 English
English 中文
中文