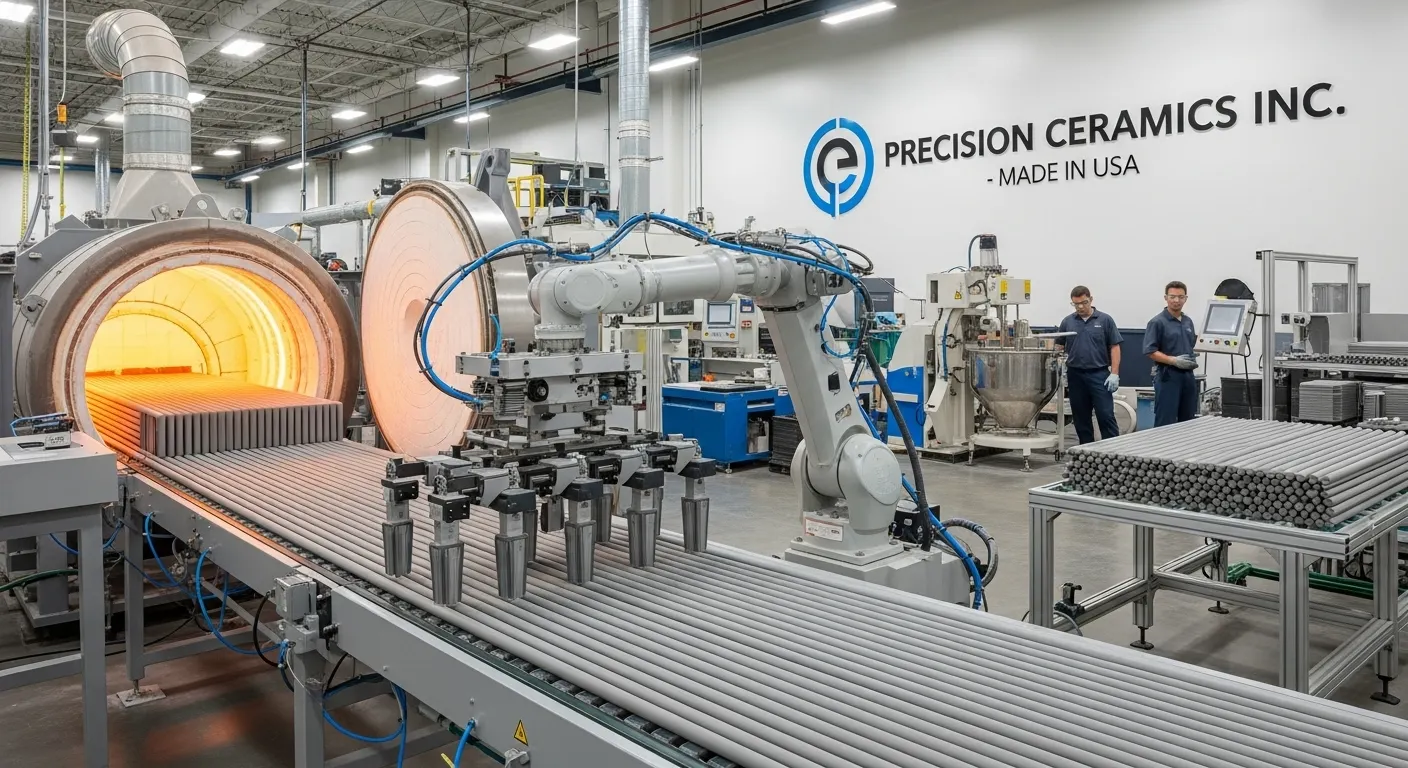
Ceramic Sleeves Manufacturer in USA
A premier ceramic sleeves manufacturer in USA serves as a critical partner for high-technology industries. These manufacturers specialize in producing small, cylindrical components with extreme precision. The primary function of a ceramic sleeve is to align critical components, most notably optical fibers. Industries from telecommunications to medicine rely on these parts. Their performance ensures data flows correctly and devices operate as designed. Understanding this technology starts with a clear ceramic sleeves guide. The quality of these components is paramount. It determines the reliability and longevity of complex systems.

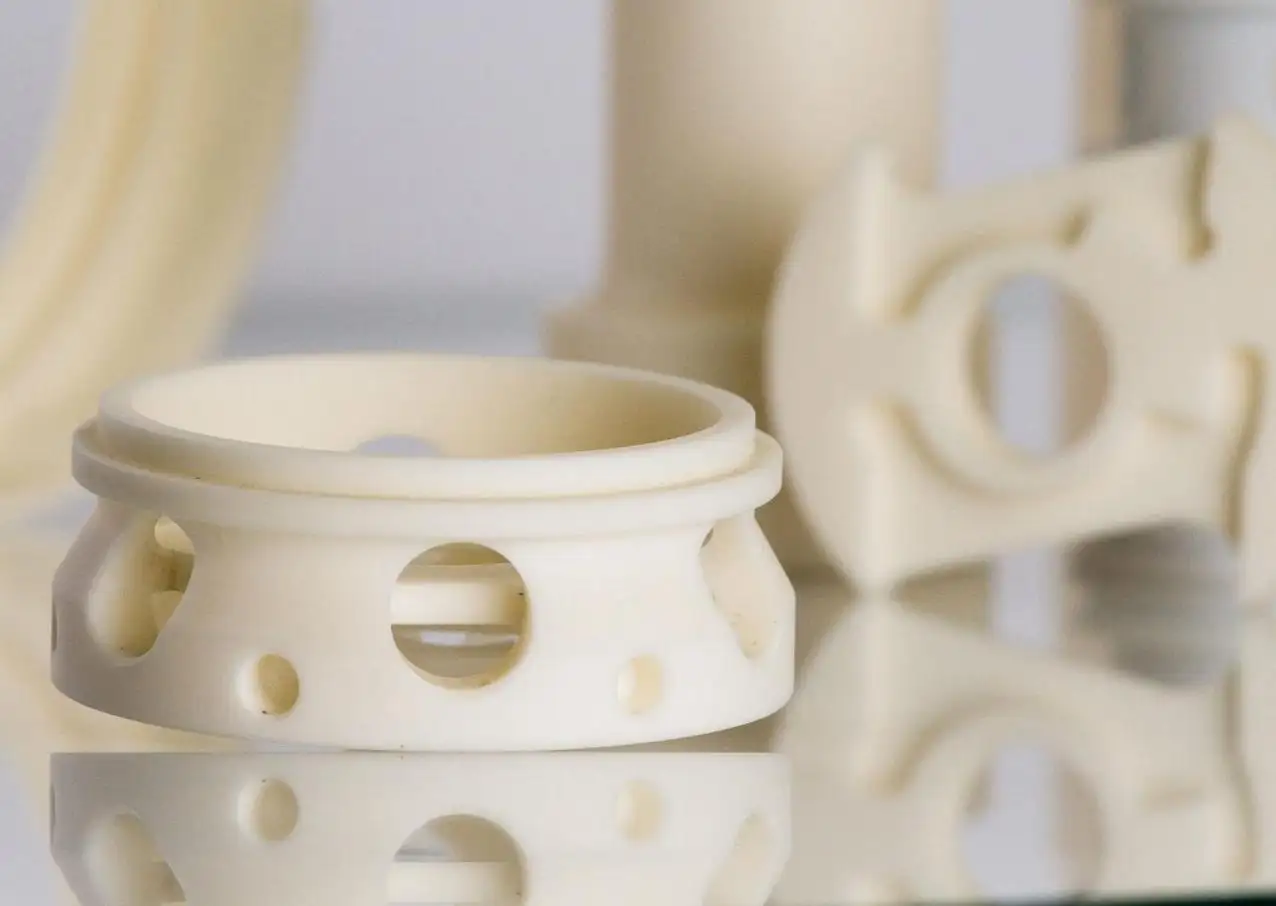
What Are High-Precision Ceramic Sleeves?
High-precision ceramic sleeves are engineered components defined by their exact dimensions. Tolerances are often measured in microns. This precision is not optional; it is the core function of the product. In fiber optics, sleeves must align two fiber cores perfectly. Even a tiny misalignment causes signal loss, known as insertion loss. Manufacturers use advanced materials, primarily zirconia, to achieve this goal. This high-precision ceramic sleeves manufacturing process is complex. It involves multiple stages of forming, sintering, and finishing. The final product is harder than steel, stable across temperatures, and non-corrosive.
The Material Science of Ceramic Sleeves
The choice of material is the foundation of a sleeve's performance. Not all ceramics are equal. The industry standard is Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (Y-TZP). This material is chosen for its unique combination of properties. It offers high fracture toughness. This means it can resist cracking under stress. It also has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. The sleeve will not change size significantly with temperature changes. This stability is vital for devices in varied environments.
Zirconia: The Industry Standard
Zirconia is the preferred material for high-performance sleeves. A zirconia ceramic sleeve provides unmatched durability and precision. Its fine-grain structure allows for an exceptionally smooth surface finish. This reduces friction and wear. Zirconia is also chemically inert. It will not react with its environment or degrade over time. Its hardness is a key benefit. It prevents the sleeve from deforming during use. This ensures a reliable connection for many years.
The Manufacturing Process for High-Precision Sleeves
Creating high-precision ceramic sleeves is a multi-step, demanding process. It begins with raw materials and ends with sub-micron inspection. Each step adds to the final component's quality and precision. US-based manufacturers control this process tightly. They manage quality from initial powder to final packaging. This ensures every sleeve meets strict industry standards.
Step 1: Raw Material Formulation
The process starts with ultra-pure zirconia powder. This powder has a particle size in the nanometer range. Manufacturers add a small amount of yttrium oxide (yttria). This oxide stabilizes the crystal structure of the zirconia. Binders are also mixed in. These organic polymers help the powder hold its shape during the next stage. The quality of this initial mix is critical. Any impurity or inconsistency can cause defects in the final product.
Step 2: Forming and Shaping
The zirconia-binder mixture is now ready for forming. The most common method is high-pressure injection molding. The mixture is heated and injected into a precise mold. This mold creates the basic shape of the sleeve, called a "green part." The green part is larger than the final sleeve. It is also porous and relatively soft. Controlling the injection pressure and temperature is key. This step ensures consistent density in the green part.
Step 3: Debinding and Sintering
The green part must undergo two thermal processes. First is debinding. The part is slowly heated in a special furnace. This heat burns away the organic binder material. The part becomes a fragile, porous ceramic. Second is sintering. The part is heated to a much higher temperature, over 1400°C. At this heat, the zirconia particles fuse. The part shrinks significantly and becomes incredibly dense. This step gives the sleeve its final hardness and strength.
Step 4: Precision Grinding and Lapping
After sintering, the sleeve is hard but not yet precise. It must be finished to exact dimensions. This is done with diamond grinding. Diamond is the only material hard enough to grind zirconia. Centerless grinding is used to finish the outer diameter (OD). Internal grinding or lapping is used for the inner diameter (ID). This is the most critical process. It establishes the sleeve's final concentricity and size. Tolerances of ±0.0005 mm are common.
Step 5: Slitting and Polishing
Many ceramic sleeves for fiber optics are "split" sleeves. A narrow slit is cut down the length of the sleeve. This slit allows the sleeve to compress slightly. It gently grips the fiber ferrule inserted into it. This action provides a firm, secure alignment. The slit is cut using diamond saws or lasers. After slitting, the sleeve may be polished. This creates a very smooth surface to prevent any scratching of the fiber.
Step 6: Quality Control and Inspection
Every sleeve must be inspected. A ceramic sleeves manufacturer in USA uses advanced metrology tools. Non-contact video measurement systems check the OD, ID, and length. Air gauges may be used to verify the inner diameter. Laser micrometers check for concentricity. Inspectors also use high-power microscopes. They look for any micro-cracks, chips, or surface flaws. Only parts that pass 100% inspection are packaged.
Types of Ceramic Sleeves Available
Ceramic sleeves are not one-size-fits-all. They are designed for specific applications and connector types. A manufacturer will offer a range of products. This includes standard-size sleeves for common connectors. It also includes fully custom parts for unique applications. The two main categories are split and solid sleeves.
Split vs. Solid Sleeves
Split sleeves are the standard for fiber optic adapters. The slit, as mentioned, allows the sleeve to flex. This provides a consistent gripping force on the ferrule. This force is essential for low-loss connections. Solid sleeves, or solid-bore sleeves, have no slit. They are rigid tubes. These are used in different applications. They serve as alignment pins, shafts, or bushings. They are valued for their rigidity and wear resistance.
Common Connector Types
In the fiber optics world, sleeves are defined by the connectors they serve. Different connectors have different ferrule diameters. The sleeve's inner diameter must match the ferrule's outer diameter perfectly. Two of the most common connector types are SC and LC.
SC Type Ceramic Sleeves
SC connectors use a 2.5 mm diameter ferrule. This was a long-time standard for telecom and datacom. An SC type ceramic sleeve supplier provides sleeves with an inner diameter built for this 2.5 mm ferrule. These sleeves are larger and very durable. Though newer, smaller connectors exist, SC remains widely used. There is a large global market for these parts, including from SC type ceramic sleeve China manufacturers.
LC Type Ceramic Sleeves
LC connectors are a smaller form factor. They use a 1.25 mm diameter ferrule. The LC connector's small size allows for much higher-density connections. This is ideal for modern data centers and network hubs. An LC type ceramic sleeve distributor stocks sleeves for this 1.25 mm ferrule. The demand for LC components is very high. This demand is met by global suppliers, including those for LC ceramic sleeve India.
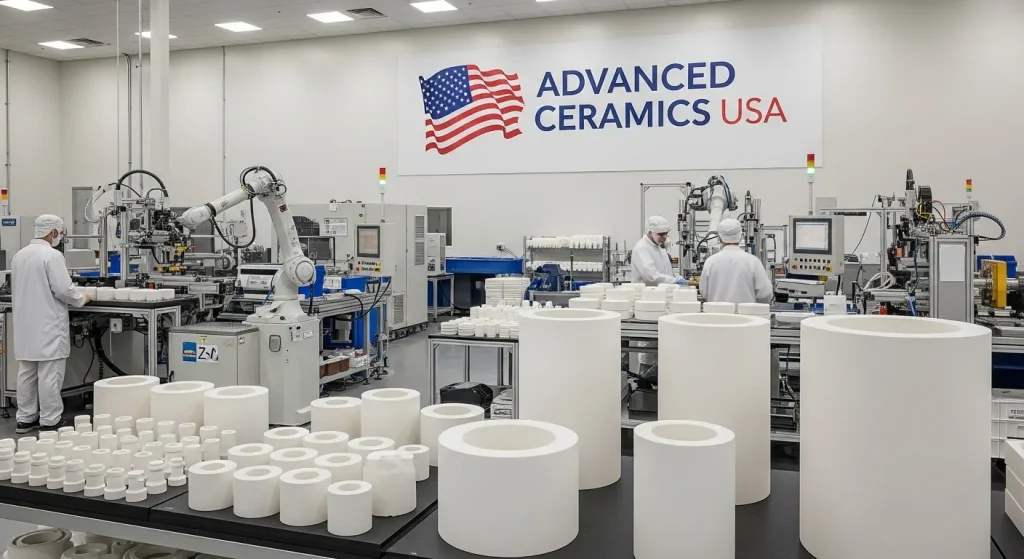
The Role of a US-Based Ceramic Sleeve Manufacturer
Choosing a ceramic sleeves manufacturer in USA provides distinct strategic advantages. For industries like defense, aerospace, and medical, the supply chain is a key concern. Domestic manufacturing provides stability, quality assurance, and better communication. It is a vital part of a secure and resilient industrial base.
Advantages of Domestic Manufacturing
Working with a US manufacturer offers many benefits.
- Supply Chain Security: It reduces dependency on long, complex overseas supply chains. This minimizes the risk of shipping delays or geopolitical disruptions.
- Reduced Lead Times: Shorter shipping distances mean faster delivery. This is critical for just-in-time inventory and rapid prototyping.
- Regulatory Compliance: US manufacturers operate under strict environmental and labor laws. They also understand US-specific standards for defense (ITAR) or medical (FDA) applications.
- Quality Oversight: It is easier to audit and visit a domestic facility. This allows for close collaboration and direct quality verification.
- Real-Time Communication: Operating in the same time zones simplifies technical support. Resolving issues or changing designs is much faster.
Top-tier manufacturers adhere to international quality standards. The most important is ISO 9001. This certification shows the company has a robust quality management system. All processes are documented, controlled, and continuously improved. For telecommunications, components often must meet Telcordia standards. These standards define the reliability and performance of network components. A good manufacturer will provide full traceability for their materials. They can provide certificates of conformity. These documents prove the material and dimensions meet the required specifications. For more information on international standards, organizations like ISO provide detailed guidelines.
Custom Manufacturing Capabilities
Many applications require non-standard solutions. This is where a true manufacturer excels. They offer custom ceramic sleeves services. A customer can provide a drawing or a set of specifications. The manufacturer's engineers will then work with them. They can advise on material choice. They can suggest design tweaks for better manufacturability. This collaboration leads to prototyping and final production. Custom capabilities can include unique lengths, wall thicknesses, or IDs. It can also involve different materials for special environments.
Key Applications for Ceramic Sleeves
While fiber optics is the largest market, it is not the only one. The unique properties of zirconia open doors to many other demanding fields. Any industry that needs precise alignment of small components is a potential user. The material's hardness, stability, and inertness are valuable assets.
Fiber Optic Interconnects
This is the primary application. Ceramic sleeves are the heart of fiber optic adapters. An adapter (or coupler) joins two fiber optic patch cords. The sleeve sits inside the adapter. It ensures the cores of the two fibers align perfectly. They are also used inside transceivers. These devices (like SFP or QSFP) send and receive light signals. Sleeves align the fiber with the laser or photodetector.
Medical Devices
Zirconia is highly biocompatible. This means it is safe for use inside the human body. It does not cause an immune reaction. This makes it an ideal material for medical instruments. It is used in surgical tools and endoscopes. It can also be used in fluid handling systems for diagnostics. The material can be sterilized repeatedly without degrading.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics industry also requires high precision. Ceramic sleeves can be used as alignment pins in semiconductor manufacturing. They help align wafers and masks during fabrication. Because they are electrical insulators, they do not short out circuits. They are also stable at the high temperatures used in some processes.
Other Industrial Uses
Other industries find value in ceramic components. A ceramic tube sleeves Indonesia supplier might stock parts for different needs. These can be used as bushings in small, high-wear mechanisms. They can act as nozzles for dispensing precise amounts of fluid. Their resistance to wear and heat makes them last longer than metal or plastic parts.
The Global Supply Chain for Ceramic Components
Ceramic sleeves are part of a large, global market. Different regions have different manufacturing strengths. A ceramic sleeves manufacturer in USA competes and cooperates within this global network. Understanding this landscape helps in making smart sourcing decisions. It highlights the importance of a balanced supply chain strategy.
Comparing Manufacturing Hubs
Manufacturing centers are located around the world. Each has a reputation for certain capabilities.
- USA: Known for high-precision, custom engineering, and stringent quality control. Strong in medical, defense, and advanced datacom markets.
- Japan: A leader in high-purity ceramic powders and advanced material science. Strong in ceramic fiber sleeves Japan and other high-tech components.
- Europe: Has strong industrial bases, particularly in ceramic sleeves Germany. Known for precision machinery and automotive-grade quality. The total ceramic sleeves Europe market is a mix of high-volume and custom work.
- Asia: Regions like ceramic sleeves China are hubs for high-volume, cost-effective manufacturing of standard components. Other areas like ceramic sleeves Indonesia support a growing electronics assembly industry. A ceramic sleeves supplier India may specialize in components for the massive domestic telecom market.
Specialized Ceramic Fiber Components
It is important to distinguish between solid zirconia sleeves and ceramic fiber components. Zirconia sleeves are dense, structural parts for alignment. Ceramic fiber products are different. They are made from woven fibers, often alumina-silica. These are used for high-temperature insulation. They are found in furnaces and heat shields. A supplier of ceramic fiber components Indonesia serves a different market, focusing on thermal management, not precision alignment.
How to Choose the Right Ceramic Sleeve Manufacturer
Selecting a supplier is a critical decision. It is a long-term partnership. The right choice ensures quality parts, reliable delivery, and good technical support. The wrong choice can lead to product failures and supply chain chaos. A thoughtful evaluation process is necessary.
What to Ask a Supplier
When you contact a potential manufacturer, ask specific questions.
- What is your primary material for sleeves? (Look for Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia, Y-TZP).
- What are your standard dimensional tolerances for ID, OD, and concentricity?
- What is your inspection process? Do you inspect 100% of parts?
- Can you provide material datasheets and certificates of conformity?
- Do you hold ISO 9001 certification?
- What are your capabilities for custom ceramic sleeves?
- What is your average lead time for standard and custom parts?
Red Flags to Watch For
Be cautious of certain responses. Vague answers are a bad sign. If a supplier cannot provide a material datasheet, do not buy from them. Be wary of prices that seem too low. This often indicates compromises in material purity or inspection. Lack of an ISO 9001 certification is a major red flag. It suggests a lack of a formal quality system. Poor communication during the sales process often predicts poor support later. Professional organizations like The American Ceramic Society promote best practices in the industry.
The Importance of a Distributor vs. Supplier
Understand the role of your vendor. A distributor stocks parts from multiple manufacturers. An LC type ceramic sleeve distributor is excellent for small quantities. They offer fast shipping for standard items. A supplier, or manufacturer, is the company that actually makes the part. An SC type ceramic sleeve supplier is the source. For large volumes or custom designs, you must work directly with a manufacturer.
The Future of Ceramic Sleeve Technology
The technology for ceramic sleeves is not static. It continues to evolve. Market trends push manufacturers to innovate. They must produce smaller, more precise, and more reliable components. Research in material science and manufacturing methods is ongoing.
Trends in Miniaturization
The entire electronics and fiber optics world is shrinking. Data centers need more connections in the same space. This drives the development of new, smaller connectors. MPO, CS, and SN connectors are examples. These high-density connectors require even smaller and more precise ceramic components. Manufacturing these parts demands tighter control over every process step.
New Materials and Composites
While zirconia is the standard, research continues. Scientists are exploring new ceramic composites. These materials might offer even greater toughness or different electrical properties. Additives can be used to change the color of zirconia. This can be used for coding parts. Detailed specifications for various technical materials are available from databases like MatWeb.
Automation in Manufacturing
Top manufacturers are increasing their use of automation. Robots can load and unload machines 24/7. This improves consistency and output. Automated visual inspection systems can check parts faster. They use AI to spot tiny defects humans might miss. This trend improves quality. It also helps keep US manufacturing competitive on a global scale. This is reinforced by quality standards from bodies like ASTM.
Conclusion: Partnering with a Premier US Manufacturer
Finding the right ceramic sleeves manufacturer in USA is essential for any high-tech company. These small components have a huge impact on system performance. They are critical for the speed of our internet, the reliability of medical devices, and the advancement of new technologies. A domestic manufacturer offers quality, stability, and expertise. They provide a secure supply chain and direct access to engineering support. By focusing on material science, a zirconia ceramic sleeve provides unmatched precision. For any project demanding the best in alignment, a partnership with a premier US manufacturer is the clear choice.
In This Article
- 1 What Are High-Precision Ceramic Sleeves?
- 2 The Manufacturing Process for High-Precision Sleeves
- 3 Types of Ceramic Sleeves Available
- 4 The Role of a US-Based Ceramic Sleeve Manufacturer
- 5 Key Applications for Ceramic Sleeves
- 6 The Global Supply Chain for Ceramic Components
- 7 How to Choose the Right Ceramic Sleeve Manufacturer
- 8 The Future of Ceramic Sleeve Technology
- 9 Conclusion: Partnering with a Premier US Manufacturer
 English
English 中文
中文