Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia
A premier Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia is a crucial partner for the nation's industrial sector. These suppliers provide high-performance components. These parts are engineered to withstand extreme conditions. This includes high heat, chemical corrosion, and electrical voltage. Standard materials like metal and plastic fail in these environments. A local supplier is a vital link. They connect the region's advanced industries with a global supply of technical ceramics. They provide local inventory, technical expertise, and quality assurance.

The industrial landscape is growing. This includes sectors like oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. The demand for reliable, high-performance materials has never been higher. A specialized supplier understands these local needs. They provide the advanced ceramic rods required for modern, efficient, and safe operations. This article explores the materials, applications, and sourcing advantages.
The Role of a Specialized Local Supplier
A local Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia is not just a reseller. They are a strategic partner. They provide several key services. These services are essential for a smooth and reliable supply chain.
Bridging Global Manufacturing with Local Industry
The manufacturing of technical ceramics is a specialized, global business. A local supplier manages this complex supply chain. They vet and audit international manufacturers. They handle all aspects of importation, customs, and logistics. This allows a local company to access world-class materials. They do this without the risks of global sourcing.
Providing Local Technical Expertise
A premier supplier has engineers on staff. They understand the materials they sell. We can read technical drawings. They can discuss a customer's specific application. This local, expert support is invaluable. They can recommend the right material for a specific task. This might be alumina for high-temperature insulation. Or it might be zirconia for high-wear components. This guidance ensures the customer gets the right part.
Managing Local Inventory for Fast Delivery
A key advantage of a local supplier is inventory. A local factory or processing plant cannot wait 12 weeks for a part. A premier supplier invests in a large, local warehouse. They stock a wide range of standard rod diameters and materials. This "just-in-time" (JIT) availability is critical. It reduces customer downtime. It allows for quick repairs and rapid prototyping.
Ensuring Quality Assurance and Vetting
The supplier acts as a quality firewall. The global market has parts of varying quality. A good supplier has an in-house quality control process. They have metrology tools. They inspect incoming batches. We check for dimensional accuracy, material purity, and defects. This vetting process ensures the customer only receives components that meet specifications.
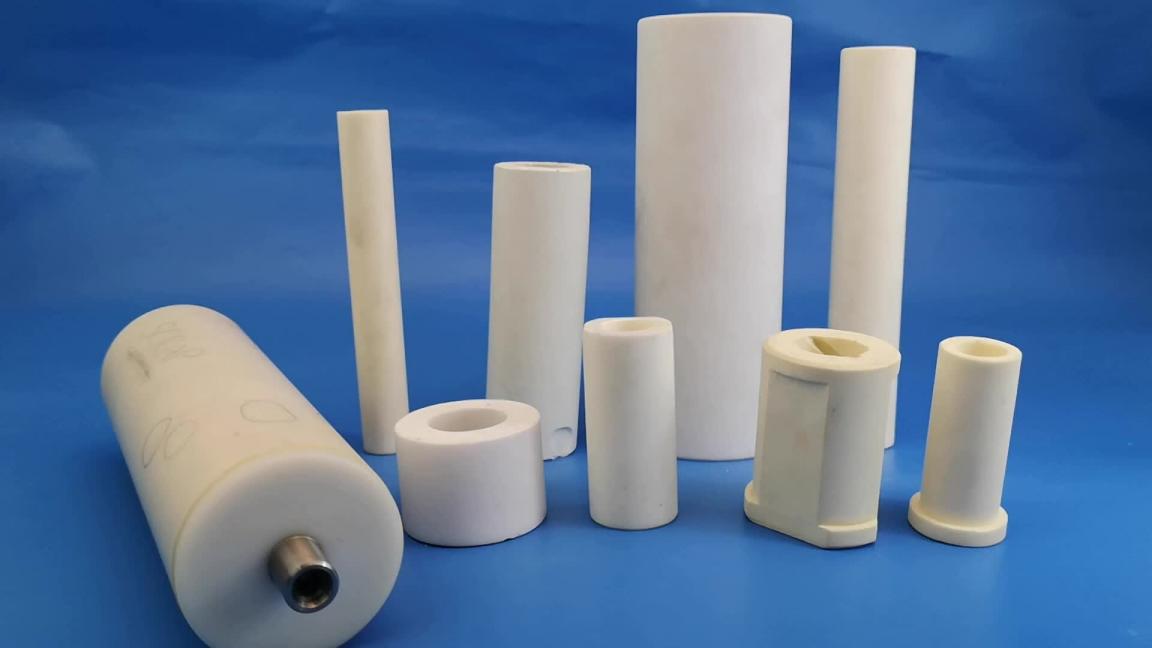
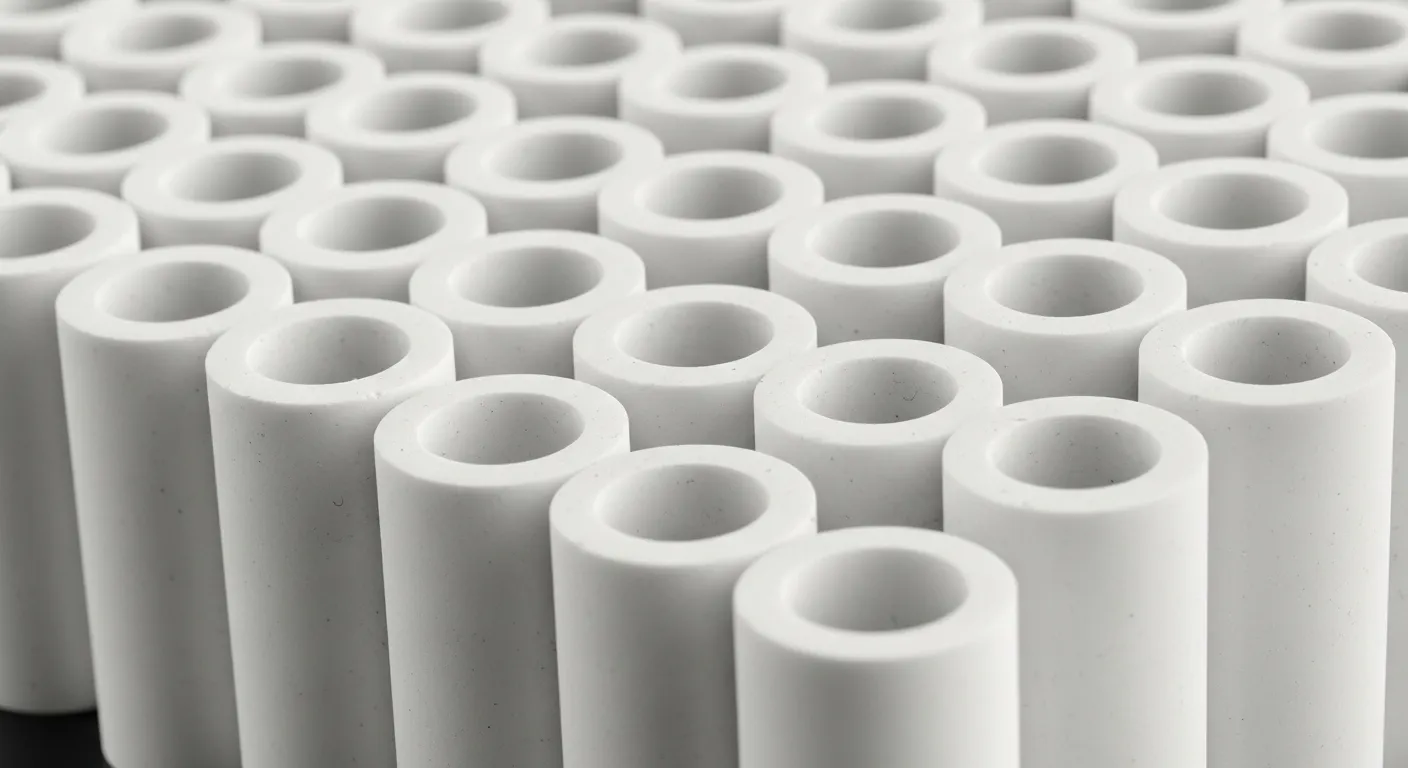
What Are Technical Ceramic Rods?
A technical ceramic rod is an engineered component. It is not the same as traditional pottery. It is made from highly purified and processed powders. This creates a dense, high-performance material. These rods can be solid cylinders or hollow tubes.
Why Use Ceramics Over Metals and Plastics?
Engineers choose ceramic rods to solve problems.
- Metals corrode, conduct electricity, and soften at high temperatures.
- Plastics have low melting points, creep under load, and degrade in chemicals.
Ceramic rods solve these problems. They are excellent electrical insulators. They are chemically inert. We maintain extreme hardness and strength at high temperatures. They provide a long, reliable service life in harsh environments.
The Importance of a Ceramic Rods Guide
The world of technical ceramics is complex. Each material has unique properties. A ceramic rods guide is an essential resource. It helps engineers understand the differences between materials. It aids in selecting the right component.
Core Materials for Industrial Rods
The properties of a ceramic rod are defined by its material. A premier Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia will offer several material options. The two most common are alumina and zirconia.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide): The Industry Workhorse
Alumina (Al2O3) is the most widely used technical ceramic. It is valued for its excellent balance of properties. It is also very cost-effective. Alumina is known for its high hardness, high compressive strength, and excellent electrical insulation. It is the default choice for many industrial uses.
Alumina Purity Grades
The properties of alumina are tied to its purity. A supplier will offer several grades.
- 95% Alumina: A common grade with a good balance of properties. It is used for wear parts and supports.
- 99% Alumina: Offers better electrical insulation and higher wear resistance.
- 99.5%+ Alumina: High-purity grades are used for medical and semiconductor applications. They offer superior chemical resistance.
Alumina is thermally conductive. It can dissipate heat. This makes it useful in some electronic applications. It is stable in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres.
Zirconia (Zirconium Oxide): The Toughness Specialist
Zirconia (ZrO2) is a premium ceramic material. It is known for one property above all: toughness. While most ceramics are hard but brittle, zirconia is different. It is stabilized with yttria (Y-TZP). This gives it a unique ability to resist cracking.
Understanding Y-TZP
The yttria in Y-TZP performs a process called "transformation toughening." If a micro-crack forms, the zirconia crystal structure changes at the tip of the crack. This change absorbs the energy. It stops the crack from growing. This makes zirconia rods incredibly durable.
Alumina vs. Zirconia: A Comparison
A technical supplier will help an engineer make this choice.
- Use Alumina for: High temperatures, electrical insulation, and wear resistance at a good cost.
- Use Zirconia for: High mechanical stress, impact resistance, and low-friction applications. Zirconia is also a thermal insulator. Alumina is a thermal conductor.
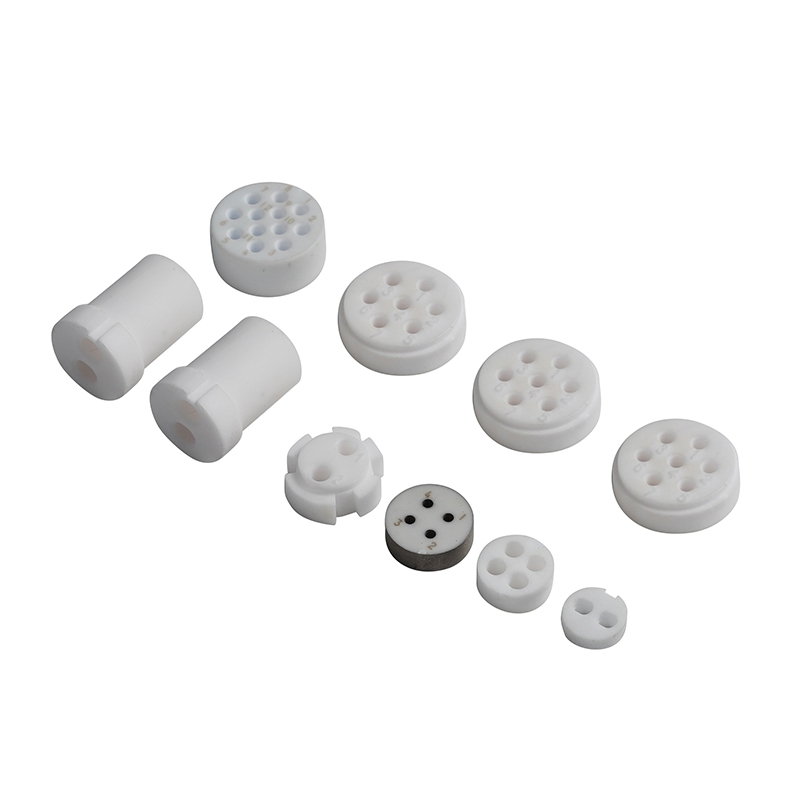
Other Advanced Materials
Suppliers may also offer more specialized materials.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Known for its extreme hardness. It has excellent thermal conductivity. It is used for high-temperature heating elements.
- Silicon Nitride (Si3N4): Has the best thermal shock resistance. It can be heated and cooled rapidly without cracking. It is used in automotive engines.
The Manufacturing Process: From Powder to Part
Ceramic rods are not cast or forged like metals. They are created from fine powders. This is a multi-stage, high-control process.
Phase 1: Raw Material Formulation
The process begins with ultra-pure ceramic powders. These powders are often in the sub-micron range. They are mixed with binders, plasticizers, and other agents. This creates a consistent, moldable slurry or paste. The quality of this initial mix is critical.
Phase 2: Forming the "Green" Part
The rod must be shaped before it is fired. This is the "green part."
- Extrusion: This is common for rods. The ceramic paste is forced through a die. The die has a circular opening. This creates a long, continuous green rod. It is then cut to length.
- Isostatic Pressing: The powder is put in a flexible mold. The mold is pressurized. This forms a very dense and uniform green part. This is good for large or complex shapes.
Phase 3: Sintering and Binder Burnout
The green rod is fragile. It is placed in a large, high-temperature furnace.
- Binder Burnout: The rod is heated slowly. The binders are burned away.
- Sintering: The temperature is raised much higher. This is often over 1600°C. The ceramic particles fuse. The part shrinks by 15-25%. It becomes incredibly hard and dense.
Phase 4: Precision Diamond Grinding
After sintering, the rod is "as-fired." Its dimensions are not yet perfect. For high-precision applications, it must be finished. The rod is now extremely hard. It can only be machined with diamond tools. This is called "hard-grinding."
- Centerless Grinding: The rod is spun between two diamond wheels. This grinds the outer diameter to a precise, uniform size. It can achieve tolerances of just a few microns.
- Lapping and Polishing: For an even smoother finish, the rod can be lapped. This is essential for sealing applications.
Key Properties of High-Strength Ceramic Rods
Engineers select ceramic rods based on specific performance data. These properties define their function.
Defining High-Strength Ceramic Rods
High strength ceramic rods are those made from advanced materials. Zirconia typically has a higher flexural strength than alumina. Silicon nitride is even stronger. This strength allows the rods to be used as structural components, not just insulators.
Mechanical Strength (Flexural and Compressive)
Ceramics are exceptionally strong in compression. They can withstand immense crushing forces. They are less strong in tension. Flexural strength is a key metric. It measures a rod's ability to resist bending.
Extreme Temperature Resistance (Thermal Stability)
This is a primary advantage. Alumina rods can be used continuously at 1500°C or more. Metal rods would melt or deform. This makes them ideal for furnace parts.
Thermal Shock Resistance
This is the material's ability to survive rapid temperature changes. Silicon nitride excels here. Alumina has a moderate resistance. Zirconia has a lower resistance.
Electrical Insulation (Dielectric Strength)
Technical ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. They have a high dielectric strength. This means they can withstand a high voltage before breaking down. This makes them ideal for power grid components.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic rods are chemically inert. They do not react with most acids, alkalis, or chemicals. This is a key advantage over stainless steel. They are used in chemical pumps and processing.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Alumina and zirconia are extremely hard. They are much harder than tool steel. In an abrasive slurry or a high-wear guide, a ceramic rod will last many times longer than a metal one.
Surface Finish and Porosity
A good ceramic rod has very low porosity. This makes it strong and non-absorbent. The surface finish can be ground smooth. This is important for seals and bearings.
Critical Applications in the Region's Industries
A Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia serves the nation's key industries. These sectors all have harsh, demanding environments.
Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical
This is a massive sector. It is filled with furnaces, reactors, and heaters.
- Furnace Linings: Ceramic components are used as furnace supports.
- Sensor Housings: Custom rods are machined to house downhole sensors. They must withstand heat, pressure, and corrosion.
- Valve Components: Custom zirconia balls and stems are used in corrosive-fluid valves.
- Pump Plungers: Zirconia plungers are used for high-pressure injection pumps.
Power Generation and Distribution
Power plants, both traditional and geothermal, use steam.
- High-Voltage Insulators: Alumina rods are used as standoff insulators. They support bus bars and other components.
- Boiler Insulation: Ceramic components are used to insulate the boiler walls and ductwork.
- Turbine Components: Ceramic parts are used in the hot sections of turbines.
Steel, Glass, and Metal Processing
The metals industry operates at extreme temperatures.
- Ladle and Tundish Liners: Ceramic components are used. They insulate the vessels that hold molten metal.
- Reheat Furnaces: Linings made of modules and blankets are used.
- Thermocouple Protection: Ceramic tubes (hollow rods) protect temperature sensors.
Pulp, Paper, and Palm Oil Manufacturing
These industries are highly abrasive and corrosive.
- Dewatering Foils: Ceramic blades and rods are used. They scrape water from the paper pulp.
- Sealing Rings: Custom-lapped zirconia rings are used in mechanical seals.
- Wear Liners: Custom ceramic parts protect machinery from abrasive palm kernels.
Advanced Research and Niche Applications
The field of ceramics is always advancing. Some materials are even processed to be clear. This creates advanced optical uses for transparent ceramics. These are used in lasers and high-tech sensors.
How to Select a Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia
Choosing the right partner is critical for success.
Verify Engineering Capabilities
A good supplier is a technical partner. Do they have engineers on staff? Can they read your drawings? Can they provide DFM feedback? A simple reseller cannot do this.
Ask About Machining Tolerances
A good supplier will be honest. They will tell you their standard tolerances. They will also tell you what is possible with precision grinding.
Demand ISO 9001 Certification
This is the baseline for a quality supplier. An ISO 9001 certification proves the company has a documented, audited quality management system. It ensures process control, material traceability, and consistency.
Request Material Data Sheets
This is the most important document. Always ask for a Technical Data Sheet (TDS). This document proves the material's properties. It lists density, hardness, flexural strength, and dielectric strength. It is the guarantee that you are getting what you paid for.
Evaluate Technical Support
A good supplier is a partner. They will help you solve your problem. They should be able to provide a ceramic rods guide to help you.
Conclusion
A Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia is a high-value, strategic partner. They are not just a vendor. They are an engineering resource. We provide the local expertise to solve complex material challenges. They manage a global supply chain. They deliver precision-engineered components. These parts allow local industries to run faster, hotter, and more efficiently. They are an investment in reliability and performance.
In This Article
- 1 The Role of a Specialized Local Supplier
- 2 What Are Technical Ceramic Rods?
- 3 Core Materials for Industrial Rods
- 4 The Manufacturing Process: From Powder to Part
-
5
Key Properties of High-Strength Ceramic Rods
- 5.1 Defining High-Strength Ceramic Rods
- 5.2 Mechanical Strength (Flexural and Compressive)
- 5.3 Extreme Temperature Resistance (Thermal Stability)
- 5.4 Thermal Shock Resistance
- 5.5 Electrical Insulation (Dielectric Strength)
- 5.6 Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
- 5.7 Wear and Abrasion Resistance
- 5.8 Surface Finish and Porosity
- 6 Critical Applications in the Region's Industries
- 7 How to Select a Ceramic Rods Supplier Indonesia
- 8 Conclusion
 English
English 中文
中文