Leading Ceramic Sleeves Supplier in India
A leading ceramic sleeves supplier in India provides the most critical component for modern fiber optic networks. These suppliers are essential partners for telecommunications, data centers, and electronics manufacturing. A ceramic sleeve is a precision-engineered tube. Its main purpose is to align two fiber optic ferrules. This alignment must be almost perfect. Any error can lead to signal loss and network failure. The quality of this tiny part determines the performance of an entire communication system.

The demand for high-speed data has grown rapidly. This growth fuels the need for reliable fiber optic components. Suppliers must deliver parts that meet exact specifications. They must also provide consistent quality in high volumes. This article explores the details of ceramic sleeves. It covers the materials, the manufacturing process, and how to select the best supplier for your needs.
What Are Ceramic Sleeves?
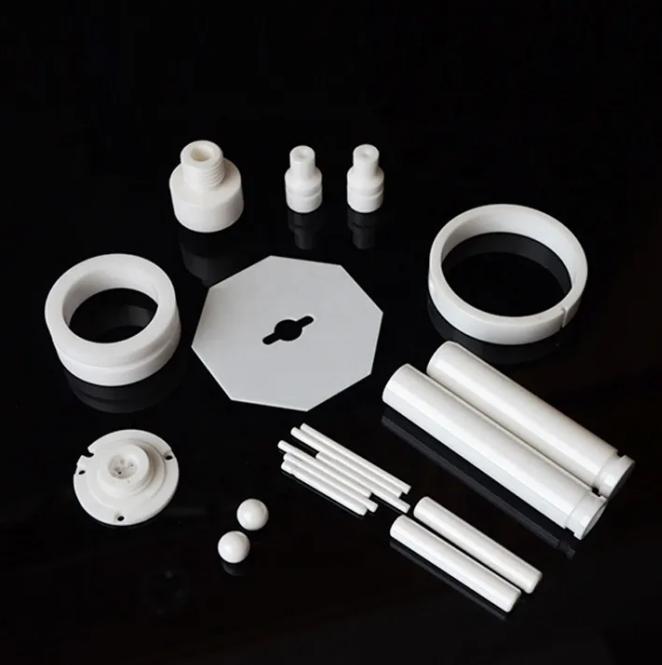
A ceramic sleeve is a small, hollow cylinder. It is also known as an alignment sleeve or split sleeve. It is a key part inside a fiber optic adapter. The adapter's job is to connect two fiber optic cables. The sleeve sits in the center of the adapter. It ensures the two fiber cores, which carry light, are perfectly aligned. This alignment is critical. The fiber cores themselves are tiny, often just 9 microns in diameter.
The Core Function of Alignment
The primary function of a ceramic sleeve is precise alignment. When two fiber ferrules are inserted into the sleeve, it holds them in a precise line. This allows light to pass from one fiber to the other with minimal loss. This loss is called "insertion loss." A high-quality sleeve minimizes this loss. It ensures a strong, clear signal. Poor alignment causes the light to scatter or reflect. This results in a weak or lost signal.
Why Are Sleeves Made of Ceramic?
Ceramic is the material of choice for high-performance sleeves. The specific material used is zirconia. This advanced technical ceramic offers many advantages over metal or plastic. Metal sleeves, like phosphor bronze, can wear out. They can deform after many connections. Plastic sleeves are less precise and less durable. Zirconia, however, is extremely hard and stable. It does not wear down easily. It provides consistent performance over tens of thousands of connections. Its properties make it the ideal material for reliable, long-term use.
Split vs. Solid Ceramic Sleeves
Ceramic sleeves come in two main designs: split and solid.
- Split Sleeves: This is the most common type for fiber optic adapters. The sleeve has a narrow slit cut down its length. This slit allows the sleeve to compress slightly when a ferrule is inserted. This compression creates a gentle, consistent grip on the ferrule. It ensures a snug fit even with tiny variations in ferrule diameter.
- Solid Sleeves: These are solid tubes with no slit. They are often called "solid-bore" sleeves. They are used in applications where a rigid, non-flexing alignment is needed. These are common in active devices like transceivers. They are also used as precision alignment pins in other industries.
The Importance of Precision Tolerances
The performance of a ceramic sleeve depends entirely on its dimensions. We are talking about "high-precision" components. Manufacturers must control dimensions to the sub-micron level. A micron is one-thousandth of a millimeter. The inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and concentricity (how centered the ID is relative to the OD) are all critical. A top-tier ceramic sleeves supplier in India must guarantee these tolerances. This commitment to precision is what separates a good supplier from a great one. A general ceramic sleeves guide can provide more background.
Zirconia: The Material of Choice
The vast majority of high-grade ceramic sleeves are made from one material. This material is Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia, or Y-TZP. It is an advanced technical ceramic. It has a unique combination of properties. These properties make it perfectly suited for fiber optic alignment.
What is Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (Y-TZP)?
Zirconia in its pure form is not stable at all temperatures. It changes its crystal structure as it heats and cools. This change causes stress and can make it crack. To solve this, manufacturers add a small amount of Yttrium Oxide (Yttria). This process is called "stabilization." The yttria locks the zirconia into a stable, strong crystal structure. This structure is known as tetragonal. The result, Y-TZP, is a material with exceptional strength and toughness. It is one of the strongest ceramic materials available.
Key Properties of Zirconia Sleeves
A ceramic sleeves supplier in India sources parts based on these properties:
- High Hardness: Zirconia is extremely hard. It is much harder than steel. This means it resists scratches and wear. Fiber optic connectors can be inserted and removed thousands of times. The sleeve will not wear out or deform.
- High Fracture Toughness: This is zirconia's most unique trait. Most ceramics are brittle. Zirconia is tough. It can absorb energy and resist cracking. This is vital for split sleeves, which must flex slightly.
- Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: Zirconia does not expand or contract much with temperature changes. This is important for network equipment. Devices can be in a hot data center or a cold outdoor cabinet. The sleeve remains stable, and the alignment stays true.
- Chemical Inertness: Zirconia does not rust or corrode. It is unaffected by moisture or other environmental factors. This ensures a long, reliable life.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Zirconia can be polished to an extremely smooth surface. This prevents it from scratching the fiber ferrule. A smooth surface also makes insertion easier.
How Zirconia Properties Impact Network Performance
These material properties directly translate to better network performance.
- Low Insertion Loss: The hardness and precision of zirconia ensure a perfect, stable alignment. This minimizes signal loss.
- High Reliability: The toughness and wear resistance mean the sleeve lasts. It provides consistent performance over the life of the network.
- Environmental Stability: The low thermal expansion and chemical inertness make zirconia sleeves reliable in any environment.
In contrast, older phosphor bronze sleeves would wear down. Each connection would shave off a tiny bit of metal. This debris could block the fiber. The sleeve itself would loosen, leading to poor alignment. Zirconia solved these problems.
The Manufacturing Process for Ceramic Sleeves
Creating a ceramic sleeve is a complex, multi-stage process. It requires specialized equipment and strict quality control. A top ceramic sleeves supplier in India works with manufacturers who have mastered this process.
Step 1: Raw Material Formulation
The process begins with ultra-pure, nanoscale powders. These are primarily zirconia (ZrO2) and yttria (Y2O3). These powders are mixed in precise ratios. An organic binder is also added. This binder is a polymer that helps the powder hold its shape. The mixture is blended until it is perfectly uniform.
Step 2: Precision Injection Molding
The powder-binder mixture is heated to form a paste. This paste is then injected under high pressure into a steel mold. This mold is a precise negative of the sleeve. This step forms the "green part." The green part is fragile. It is also larger than the final sleeve. It is larger because it will shrink during a later step.
Step 3: Debinding
The green parts are carefully placed in a special furnace. This furnace slowly heats the parts in a controlled atmosphere. This process is called debinding. The heat burns away the organic binder. This must be done slowly. If heated too fast, the part could crack or warp. After debinding, the part is a porous, chalky object made only of ceramic powder.
Step 4: Sintering
The debound parts go into a high-temperature furnace. They are heated to over 1,400 degrees Celsius. This is the sintering stage. At this high heat, the ceramic particles fuse. The part shrinks, becoming incredibly dense and hard. This step gives the sleeve its final, rock-hard ceramic properties. The part shrinks by a predictable amount. The initial mold is designed to account for this shrinkage.
Step 5: Precision Grinding and Lapping
After sintering, the sleeve is hard, but its dimensions are not yet perfect. It must be finished. This is the most critical stage for precision.
- Centerless Grinding: The outer diameter (OD) is ground to its exact size. This is done using diamond grinding wheels.
- Lapping: The inner diameter (ID) is finished. This is a very fine polishing process. It uses a diamond slurry to slowly remove material. This lapping creates the final, precise ID and the smooth surface finish.
Step 6: Slitting and Chamfering
If the sleeve is a split-type, it now goes to a cutting station. A very thin diamond saw or laser cuts the narrow slit down its length. The ends of the sleeve are also chamfered. This means a small, angled edge is cut. This chamfer helps guide the ferrule into the sleeve. It prevents the sharp edge from chipping or scratching.
Step 7: Final Inspection and Quality Control
Every single sleeve must be inspected. A ceramic sleeves supplier in India must verify this. Manufacturers use advanced inspection tools.
- Video Measurement: Non-contact cameras check the length and OD.
- Air Gauges: These tools blow air through the sleeve. By measuring the airflow, they can determine the inner diameter with sub-micron accuracy.
- Visual Inspection: Human inspectors or AI systems check for any visual flaws. They look for cracks, chips, or surface defects.
Only parts that pass all inspections are packaged and sold.
Common Types of Ceramic Sleeves
A ceramic sleeves supplier in India stocks sleeves for various connector types. The type is defined by the ferrule diameter it is designed to hold. The two most common types are SC and LC.
SC Type Ceramic Sleeves
SC (Subscriber Connector) sleeves are designed for SC connectors. These connectors use a 2.5 mm ferrule. The SC connector was a standard for many years. It is still widely used in telecommunications and data networks. An SC type ceramic sleeve supplier provides sleeves with an inner diameter built for this 2.5 mm ferrule. These sleeves are larger and very robust. The global supply chain for these parts is well-established. It includes major manufacturing hubs, like those for SC type ceramic sleeve China.
LC Type Ceramic Sleeves
LC (Lucent Connector) sleeves are for LC connectors. These connectors use a smaller 1.25 mm ferrule. The LC connector's small size allows for much higher connection density. This is why it is the standard for modern data centers. Racks are filled with equipment. The LC connector allows more connections in the same small space. The demand for LC ceramic sleeve India components is driven by this data center boom. A reliable LC type ceramic sleeve distributor is a key partner for data center builders.
Other Connector Types
While SC and LC are the most common, other types exist.
- ST (Straight Tip): Also uses a 2.5 mm ferrule, but with a bayonet-style connector.
- FC (Ferrule Connector): Uses a 2.5 mm ferrule with a threaded connector.
- MPO/MTP: These are multi-fiber connectors. They align 8, 12, or 24 fibers at once. They use precision pins and holes, not a central ceramic sleeve.
A full-service supplier will have knowledge of all these types.
How to Select a Ceramic Sleeves Supplier in India
Choosing the right supplier is a critical business decision. It is not just about the lowest price. The supplier becomes a part of your supply chain. Their quality and reliability directly affect your products.
Key Criteria for Evaluation
When you evaluate a ceramic sleeves supplier in India, consider these factors:
- Product Quality: Do they use Y-TZP zirconia? Can they provide material datasheets? What are their standard dimensional tolerances?
- Quality Management: Is the supplier or their manufacturer ISO 9001 certified? This shows they have a documented, repeatable quality system.
- Technical Expertise: Can you talk to an engineer? Do they understand your application? Can they help you solve a technical problem?
- Inspection and Testing: Ask about their quality control process. Do they 100% inspect parts? Can they provide inspection reports with your order?
- Customization: Can they provide custom ceramic sleeves? Your project may need a special length or a unique ID.
- Supply Chain and Lead Time: Do they keep stock? What are their lead times for standard and custom orders? A local supplier can offer much faster delivery.
Understanding Quality: ISO 9001
Always look for suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified. This is an international standard for quality management. You can learn more from the International Organization for Standardization. This certification is not just a piece of paper. It means the company has been audited. It proves they have processes for manufacturing, inspection, and continuous improvement. A certified supplier is a safer, more reliable partner.
The Value of Technical Support
A good supplier is more than a reseller. They are a technical partner. They should have staff who understand the product. You should be able to ask them, "What is the insertion loss performance of this sleeve?" or "What is the recommended ferrule tolerance for this ID?" Their answers will tell you a lot about their expertise. A supplier who only talks about price may not be able to help you when a technical problem arises.
Red Flags: What to Avoid
Be cautious of suppliers who:
- Cannot provide a material datasheet.
- Are not ISO 9001 certified.
- Are vague about their inspection process.
- Offer a price that is significantly lower than all others. This often indicates a compromise on material quality (e.g., using cheaper alumina or lower-grade zirconia).
- Have poor communication. If they are slow to respond now, they will be slow when you have a problem.
Distributor vs. Manufacturer
It is important to know if you are talking to a distributor or a manufacturer.
- A Distributor (or supplier) stocks parts from one or more manufacturers. They are good for smaller quantities and fast delivery of standard parts.
- A Manufacturer is the company that actually makes the sleeve. You would work directly with a manufacturer for very large volumes or for highly custom designs.
A leading ceramic sleeves supplier in India often has a hybrid role. They may be an exclusive distributor for a major manufacturer. They may also have their own secondary processing or quality-checking facilities.
The Global Context of Sourcing
The supply chain for ceramic components is global. Major manufacturing hubs exist around the world. There are large markets for ceramic sleeves China and ceramic sleeves Germany. Other regions, like for ceramic sleeves Indonesia, also have a growing demand. Sourcing from a local supplier in India helps navigate this global network. They can manage importation, customs, and quality control. This simplifies your procurement process.
Key Applications of Ceramic Sleeves
The use of ceramic sleeves extends beyond just network cables. Their precision and durability make them valuable in several high-tech fields.
Fiber Optic Adapters
This is the largest application. Every fiber optic adapter, or coupler, has a ceramic sleeve at its core. These adapters are used in:
- Patch panels in data centers.
- Wall outlets for Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH).
- Network equipment connection points.
Active Devices and Transceivers
Fiber optic transceivers are the devices that send and receive light signals. Examples include SFP, SFP+, and QSFP modules. These modules connect a fiber optic cable to the electronics. Inside, a ceramic sleeve is often used. It aligns the incoming fiber with the tiny laser or photodetector. This alignment must be perfect.
Medical Devices
Zirconia is biocompatible. This means it is non-toxic and does not cause a reaction in the human body. It can also be repeatedly sterilized. This makes it a valuable material for medical tools. Ceramic sleeves can be used in:
- Endoscopes and fiber optic scopes for surgery.
- Laser delivery systems for surgical procedures.
- Connectors for medical sensing equipment.
Industrial Sensing and Lasers
Many industrial sensors use fiber optics. They can measure temperature, pressure, or vibration. These sensors need reliable connectors that can survive harsh factory environments. High-power industrial lasers also use fiber optic cables. The connectors for these systems use ceramic sleeves. They must handle high power and high temperatures.
Conclusion: Your Partner for Precision
A ceramic sleeves supplier in India is a key enabler of modern technology. These tiny components are the unsung heroes of the digital age. They ensure our data flows quickly and reliably. When selecting a supplier, look beyond the price. Focus on quality, precision, and expertise.
The best supplier is a partner. They understand the material science of zirconia. They have a deep knowledge of the manufacturing process. We are committed to quality, proven by their ISO 9001 certification. By choosing a leading ceramic sleeves supplier in India, you are building a foundation for quality. You are ensuring your own products and networks perform at the highest level.
 English
English 中文
中文